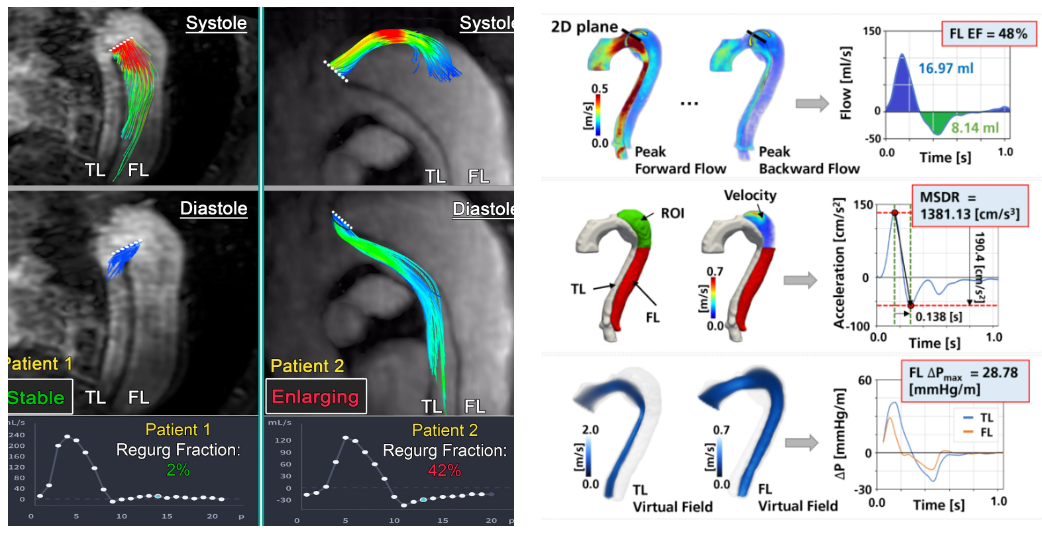
4D Flow in Aortic Dissection
4D Flow MRI is an advanced imaging technique that enables dynamic 3D measurement of blood flow in the aorta and other large vessels. Our group applies this method to study aortic dissection (AD), a condition that creates two flow channels—true and false lumens—and is linked to complex anatomy and poor long-term outcomes. Our studies show that distinctive blood flow and pressure patterns in the false lumen may help identify patients at highest risk for aortic growth and the need for surgical repair.This work has been supported by prior and current grants from the Radiologic Society of North America and the NIH National Heart Lung & Blood Institute (R01HL170059).
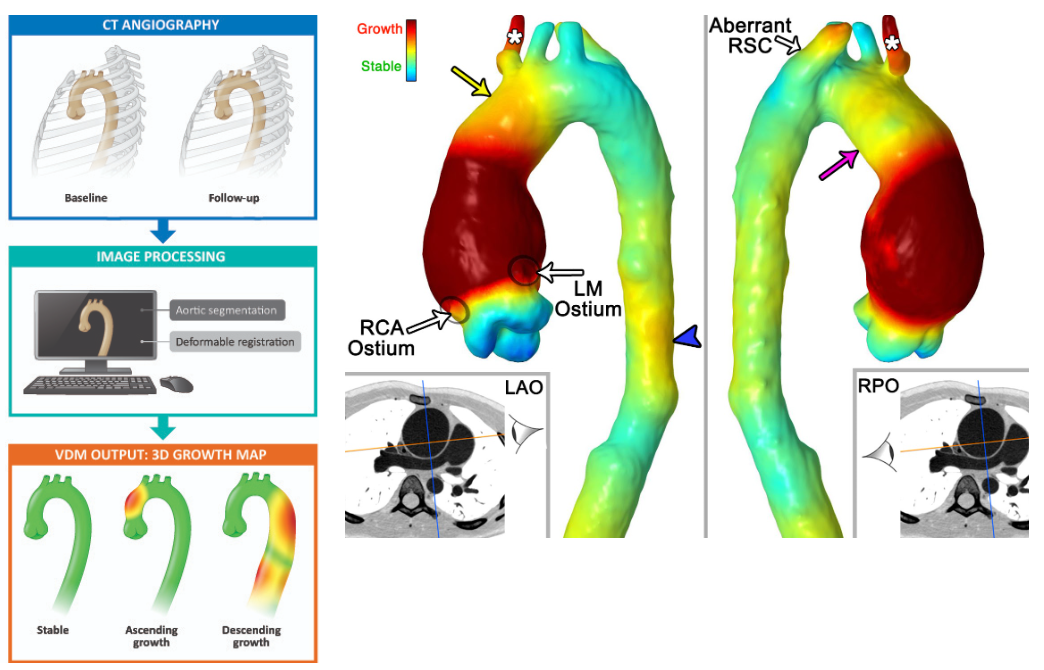
Vascular Deformation Mapping (VDM)
Vascular Deformation Mapping is an image analysis technique recently developed in our lab that takes routine gated computed tomography angiography (CTA) data and performs an analysis of 3-dimensional aortic growth in a matter that is more comprehensive and accurate than can be achieved with standard manual diameter-based measurements. We have validated this technique and are currently investigating VDM’s uses for better understanding growth patterns, predicting future growth & adverse events and assisting with surgical planning. VDM has been developed in conjunction with industry partners though the support of an NIH Small Business Innovation Research grant (R44HL145953)
Deep Learning for Automated Aortic Segmentation and Analysis
Segmentation and manual measurement of the aorta are time consuming tasks, even for expert readers, but are central components in most aortic analyses. These tasks can be greatly accelerated through image analysis techniques such as deep learning (DL). We are focused on developing and optimizing DL techniques to assist with aortic image analysis though a variety of tasks including automated aortic measurements and registration. The objective of this work is to make aortic image analysis more accurate, efficient and reproducible, and to advance the automation of other algorithms being developed in the lab.
